
However, in two- and three-dimensional kinematics, even if the speed is a constant, a particle can have acceleration if it moves along a curved trajectory such as a circle. Precession: he change in orientation of an object’s rotational axis and is the result of conservation of momentum.In one-dimensional kinematics, objects with a constant speed have zero acceleration. Use the equations of circular motion to find the position, velocity, and. Just like linear momentum, angular momentum is always conserved. Solve for the centripetal acceleration of an object moving on a circular path. What is Circular Motion The motion of a body such that its distance from a particular point remains constant is known as circular motion.
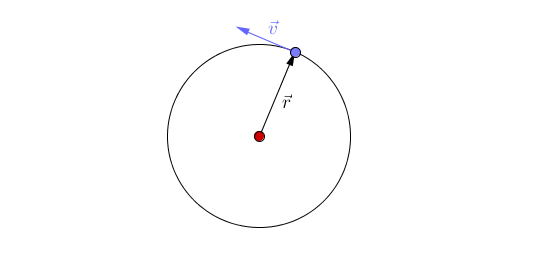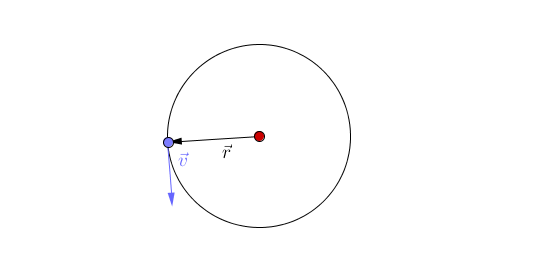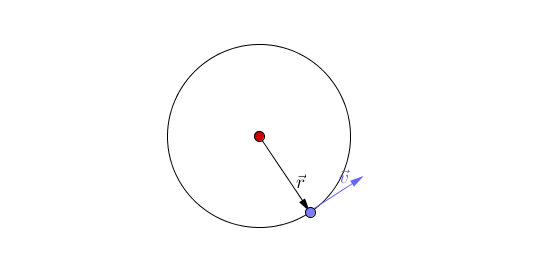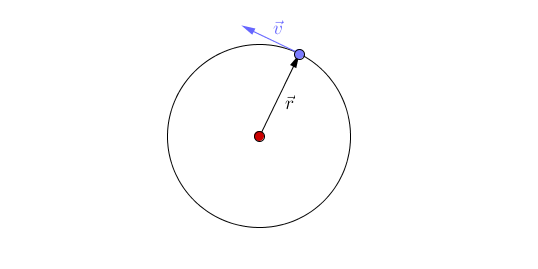
The object travels around a curved path and maintains a constant radial distance from the center point at any given time. Linear/Tangential Velocity Objects moving in a circle still have a linear velocity distance/time. If the axis of rotation is outside the object, the object is revolving. If the axis of rotation is inside the object, the object is rotating (spinning). m.Īngular Momentum (L): he measurement of a rotating object’s inertia. The simplest case of circular motion is uniform circular motion, where an object travels a circular path at a constant speed. Uniform circular motion defines the motion of an object traveling at a constant speed around a fixed center point or axis. Circular Motion Terms The point or line that is the center of the circle is the axis of rotation.Similar to how forces cause an acceleration, torques cause an angular acceleration. Torque (τ): A measurement of the ability for a force to rotate the object that it is acting on. An object that moves in a circular motion will have the same average velocity and altitude of an object in an elliptical orbit. From planning satellites orbits around the earth to designing thrilling amusement park rides, understanding circular motion and gravity allows you to calculate, explain, and predict how pretty much anything that moves in a circle. Moment of Inertia is the angular equivalent of mass. The motion of an object moving around a circle at a constant speed can be modeled as follows. Moment of Inertia (I): A measurement of an object’s stationary inertia with respect to rotational motion. When the car is taking a turn on the road, a total of three forces act simultaneously on the car: The weight of the car, mg. Called tangential speed because the direction of motion is always tangent to the circular path.Īngular Acceleration (α): The rate at which an object’s angular velocity is changing. The motion of a car on a level road: Let us assume a car is moving on a level road, with mass ‘m’ and ‘g’ as the acceleration due to gravity acting upon it. Tangential Speed: The linear speed of a rotating object. Lets learn about the meaning of motion, circular motion, the. SI units: radĪngular Velocity (ω): The rate at which an object rotates around a central axis. Circular motion is a motion in which a body travels a definite distance along a circular path. SI units: NĪngular Displacement (θ): The angle that an object has moved around a central axis. A centripetal force causes a centripetal acceleration, represented as \(a_c\). of the motion r, the angular speed, the period T, and the rotational frequency f. The velocity of an object in UCM constantly changes, because its. Centripetal Force: A centripetal force is any constant force that causes an object to rotate in a circle. Uniform circular motion is the motion of an object traveling at a. A body exhibits uniform circular motion (UCM) when it moves in a circle at a constant speed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
